Manage your PC Temperature using the TDP
Jun 08, 2017Fans are designed to cool down computers and ensure that the heat inside your PC does not get too intense but run your applications properly. So how can you cool down (or manage the temperature of) a PC that does not have fans (like ours)? We describe one way to do it in this blog!
What generates Heat on a PC?
The heat on a PC is generated mainly by the CPU. The higher heat generated by the processor, the higher temperature your PC will get. On our Fanless PCs, the heat is dissipated by the design itself: the full die cast aluminium case is working as a Heat Sink itself. That’s why it’s called passive cooling. It doesn’t mean that all heat will be dissipated but your PC will run perfectly.
As the heat comes mainly from the processor, CPU types help to manage the overall heat of your system. For instance, mobile processors are often preferred to desktop processors as they generate less heat and have a lower power consumption.
When can a Fanless PC overheat?
There are cases where your PC can get too hot. For example, if your software is complex, your CPU and GPU can be very solicited and will generate heating while working. The CPU temperature will raise and the overall temperature of your PC will follow (but at a lower temperature thanks to the passive cooling).
If your PC is running an application in a hot environment (outdoor at 40◦C), the passive cooling will also be impeded – meaning it will become less efficient to cool down than under a “normal” temperature environment (office at 20◦C).

Our Lab conducting heat tests for customers' projects.
Cooling down via the Thermal Design Power (TDP)
Do you know that you can improve the cooling by reducing the Thermal Design Power (TDP) of your PC? The TDP gives the maximum amount of heat generated by a computer chip or component. For example, if the TDP of Fitlet RM is 10W, then it would be set at 10,000 in the BIOS by default.
The Thermal Design Power serves as the nominal value for designing CPU cooling systems and can be modified in the BIOS. Depending on your application, you could, for example, set it up 4,500 as a minimum (BIOS > Power Settings > APU TDP) and run your application again to measure the difference.
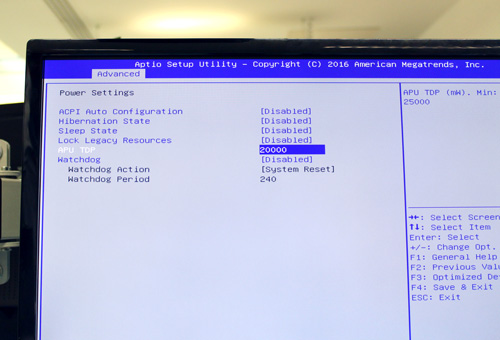
Screenshot of the BIOS: 2000 means 2W TDP
Ask for Technical Expertise
This is a way to do it. There are other ways to cool down the PC as using a specific Heat Sink to push the passive cooling. In any cases, we ask our customers to talk with our engineers first so they can discuss applications with you and provide the best technical expertise – whether it is before deploying your project or optimising your portfolio.
Articles related to this topic:
Comparing Mobile CPU and Desktop CPU
How does Fanless Technology work?
The best way to reduce your system's power consumption
 Part of
Part of